We rely on our hearing to connect with friends and family, listen to our favorite music, alert us to safety information and more. Understanding how we perceive sound and the potential hazards to our hearing empowers us to safeguard this precious sense. Let’s explore the mechanics of hearing and identify some common causes of hearing loss.
The Mechanics of Hearing
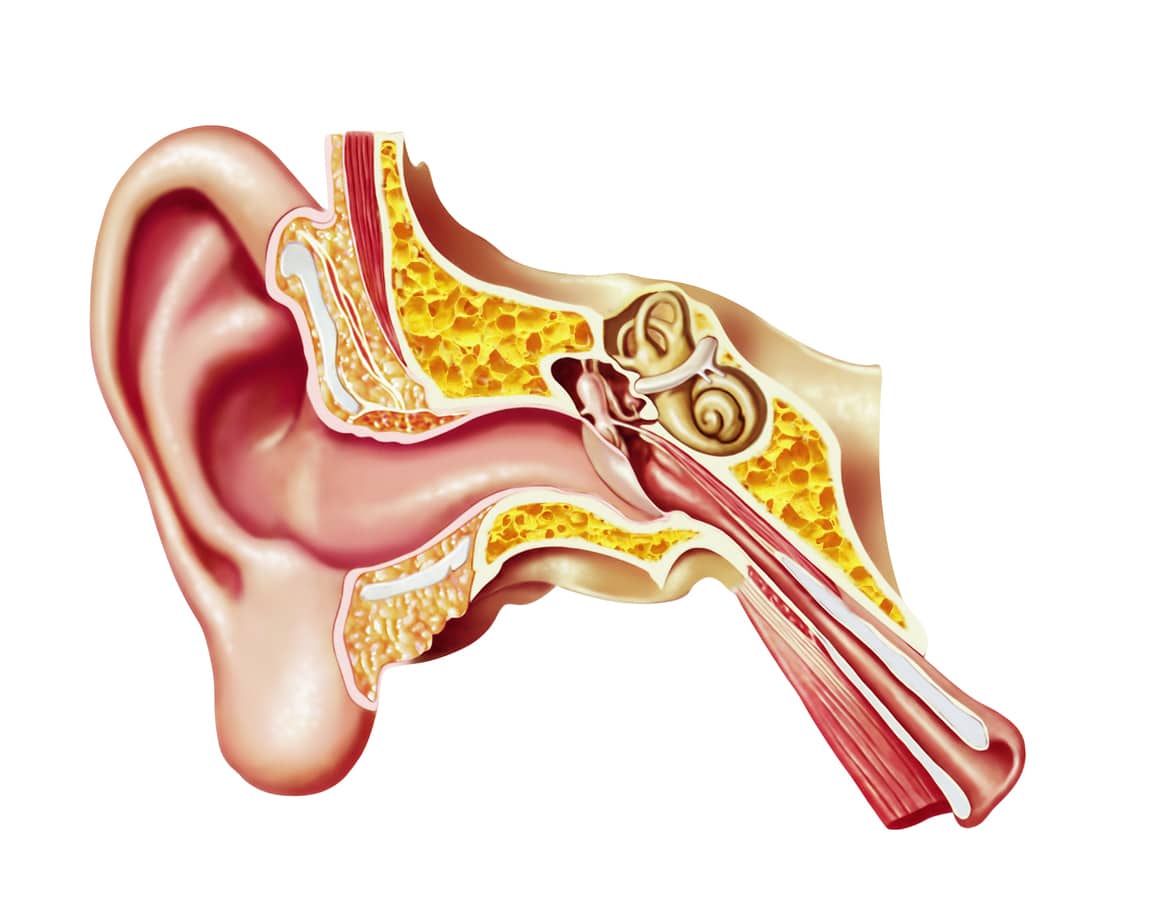
When you’re sitting in Jasmine Park, basking in the spring sun, and someone yells “DUCK,” you instantly grasp the information, allowing you to dodge an errant frisbee. But behind the seemingly instantaneous act of hearing lies a complex process.
When the Frisbee thrower yells “DUCK,” the sound waves head through the air, entering your outer ear. These waves hit your eardrum, causing it to vibrate. The tiny bones in your middle ear, known as ossicles, amplify these vibrations before transmitting them to the inner ear. Once inside the inner ear, the amplified vibrations journey into the cochlea, a fluid-filled structure adorned with approximately 16,000 microscopic hair cells. As the vibrations ripple through the cochlea’s fluid, they set these hair cells in motion. This movement generates electrical signals, which are then relayed to the brain via the auditory nerve. In the brain, these electrical signals are decoded into the sounds we understand, in this case, the word “duck.”
What Gets in the Way of Hearing?
Hearing loss arises when any part of this intricate process encounters disruption. Several factors can interfere with the process, including:
- Aging. Natural changes in the inner ear’s structure with age can lead to a gradual decline in hearing.
- Exposure to loud noise. Prolonged exposure to loud noises can strain and damage the hair cells in the inner ear, resulting in temporary or permanent hearing loss.
- Ototoxic medications. Certain medications risk damaging the auditory system, potentially causing hearing loss or tinnitus. There are over 200 known ototoxic medications, but a few common ones include chemotherapy drugs, blood pressure medication and over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Illness. Infections and medical conditions like otosclerosis, acoustic neuromas, Ménière’s disease and ear infections can cause damage, leading to hearing loss.
Tips To Prevent Hearing Loss
Not all causes of hearing loss are preventable. For instance, you cannot stop aging or prevent every illness. But there are a few ways you can help safeguard your hearing, including:
- Use ear protection in noisy environments and lower the volume when possible.
- Discuss known ototoxic medications with your provider. While some ototoxic medications cannot always be avoided, like those used to treat cancer or severe hypertension, it is a good idea to discuss your options. Even if there is no alternative to an ototoxic medication, knowing the possible side effects can help you prepare.
- Schedule regular audiology appointments to help monitor your hearing health and identify issues early on.
To learn more about caring for your hearing health or treating hearing loss, contact Lake Jackson ENT & Med Spa to schedule an appointment with one of our providers.